TCP port 22 is one of the most important ports in modern computer networks. It is the default port used by SSH (Secure Shell), a protocol designed to provide secure remote access to systems over an untrusted network. Whenever engineers connect to a server, network device, or industrial system using SSH, they are almost always using TCP port 22.
In IT, industrial, and SCADA environments, TCP port 22 plays a critical role in device configuration, troubleshooting, and diagnostics. It allows administrators and engineers to securely access remote systems without exposing sensitive data.
Table of Contents
What Is TCP Port 22?
A TCP port is a logical endpoint that allows network services to communicate. TCP port 22 is officially assigned to the SSH protocol. When a device listens on TCP port 22, it is waiting for incoming SSH connections.
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. This means it ensures data is delivered reliably, in order, and without duplication. When SSH uses TCP port 22, it benefits from this reliability while adding strong encryption and authentication on top.
In practical terms, TCP port 22 is the “door” that SSH uses to accept secure remote connections.
What Is SSH and Why It Uses TCP Port 22
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a protocol that allows users to remotely log in to another system and execute commands securely. Before SSH existed, remote access was often done using insecure protocols that sent usernames and passwords in plain text.
SSH was designed to solve this problem. It encrypts all traffic between the client and the server, protecting credentials, commands, and output from being intercepted. TCP port 22 was assigned to SSH as its default communication port, and it has remained the standard ever since.
When an SSH client connects to a device, it opens a TCP connection to port 22, negotiates encryption, authenticates the user, and then establishes a secure session.
How TCP Port 22 and SSH Work Together
When a connection is made to TCP port 22, several steps take place. First, a TCP connection is established between the client and the server. This ensures reliable communication. Next, the SSH protocol begins its handshake process.
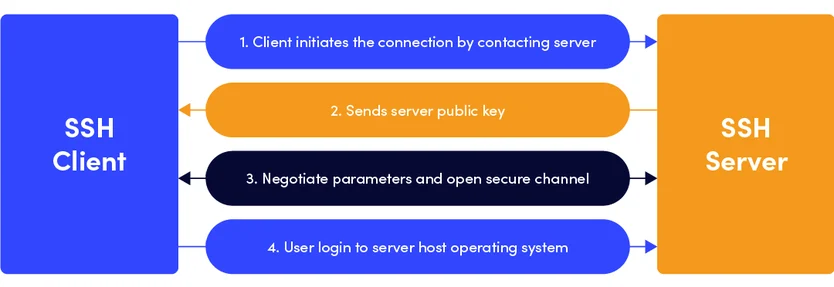
During this handshake, the client and server agree on encryption algorithms and exchange cryptographic keys. The server proves its identity, and the user authenticates using a password or an SSH key. Once this process is complete, a secure, encrypted tunnel is created.
From that point on, all data sent through TCP port 22 is encrypted. Commands, configuration changes, and diagnostic outputs are protected from eavesdropping or tampering.
Importance of TCP Port 22 for Device Configuration
One of the most common uses of SSH over TCP port 22 is device configuration. Engineers and administrators rely on SSH to configure servers, network devices, and industrial equipment remotely.
Using SSH, they can edit configuration files, apply updates, restart services, and adjust system settings without being physically present. This is especially important in environments where devices are located in remote or hard-to-access locations, such as substations, factories, or data centers.
TCP port 22 enables this work to be done securely. Without encryption, configuration commands could be intercepted or modified, leading to security risks or system failures.
Role of TCP Port 22 in Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is another area where TCP port 22 is essential. When a system is not behaving as expected, engineers often need direct access to logs, processes, and system status information.
SSH provides an interactive command-line interface that allows detailed inspection of a device. Through TCP port 22, engineers can check running services, view error logs, monitor resource usage, and test network connectivity.
Because SSH sessions are encrypted, sensitive diagnostic information is not exposed to the network. This is particularly important in industrial and critical infrastructure environments, where information leakage can pose serious risks.
TCP Port 22 and Remote Diagnostics
Diagnostics often require more than just viewing information. Engineers may need to run test commands, capture system data, or temporarily change configurations to isolate a problem.
SSH over TCP port 22 makes this possible in a controlled and secure way. Diagnostic commands can be executed in real time, and their results can be reviewed immediately. This reduces downtime and allows faster response to incidents.
In many cases, SSH is also used to securely transfer diagnostic files, such as logs or configuration backups, from a device to a central system for further analysis.
Importance of SSH for Industrial and SCADA Devices
In industrial and SCADA environments, SSH has become the standard method for secure remote access to gateways, controllers, and supporting servers. While real-time control traffic may use specialized protocols, SSH is commonly used for management and maintenance.
TCP port 22 allows engineers to safely access devices that control critical processes. Configuration changes, firmware updates, and system checks can be performed without interrupting operations.
Because these systems often control physical processes, security is essential. SSH ensures that only authorized users can access devices and that all management traffic is protected.
Security Considerations for TCP Port 22
Because TCP port 22 is widely known, it is also a common target for attacks. Automated scanning tools frequently look for systems that expose port 22 to the internet.
For this reason, systems using SSH must be properly secured. Strong authentication methods, such as SSH keys, should be used instead of simple passwords. Access to TCP port 22 should be restricted using firewalls, allowing only trusted networks or IP addresses.
In sensitive environments, SSH access is often combined with VPNs and network segmentation to further reduce exposure.
Can TCP Port 22 Be Changed?
SSH does not have to use TCP port 22. Administrators can configure SSH to listen on a different port. This can reduce the amount of automated attack traffic, but it does not replace proper security controls.
Even when a different port is used, the same security principles apply. Strong authentication, access controls, and monitoring are still required. The importance of TCP port 22 lies not just in the port number itself, but in how SSH is configured and managed.
Why TCP Port 22 Remains Essential
Despite new technologies and management tools, TCP port 22 remains essential because SSH is simple, reliable, and universally supported. Almost every operating system and network device includes an SSH client and server.
This universality makes SSH the preferred tool for remote access, configuration, troubleshooting, and diagnostics. TCP port 22 acts as a standard entry point, making it easier to design, document, and secure network architectures.
In industrial environments, where reliability and long-term support matter, this stability is especially valuable.
SSH Software Tools That Use TCP Port 22
To connect to devices using SSH over TCP port 22, engineers use SSH client software. These tools allow users to open a secure session, run commands, and perform configuration or diagnostics on remote systems.
One of the most widely used SSH tools is PuTTY.
PuTTY is a popular SSH client, especially on Windows systems. It provides a simple interface for connecting to remote devices using SSH over TCP port 22.
When using PuTTY, the user enters:
- The IP address or hostname of the device
- The connection type (SSH)
- The port number (22 by default)
PuTTY then opens a TCP connection to port 22 and starts the SSH handshake process. Once authentication is complete, the user gains secure command-line access to the remote system.
PuTTY is commonly used for:
- Initial device setup
- Configuration changes
- Troubleshooting system issues
- Viewing logs and diagnostic information
Because PuTTY uses SSH, all traffic sent through TCP port 22 is encrypted.
How to Use PuTTY to Access a Server Using SSH
Once PuTTY is installed and you have your SSH connection details, you can begin the connection process.
Start by launching the PuTTY application. In the main configuration window, enter the server’s IP address or hostname in the Host Name field. In the Port field, enter the SSH port number, which is typically 22. Make sure the connection type is set to SSH.
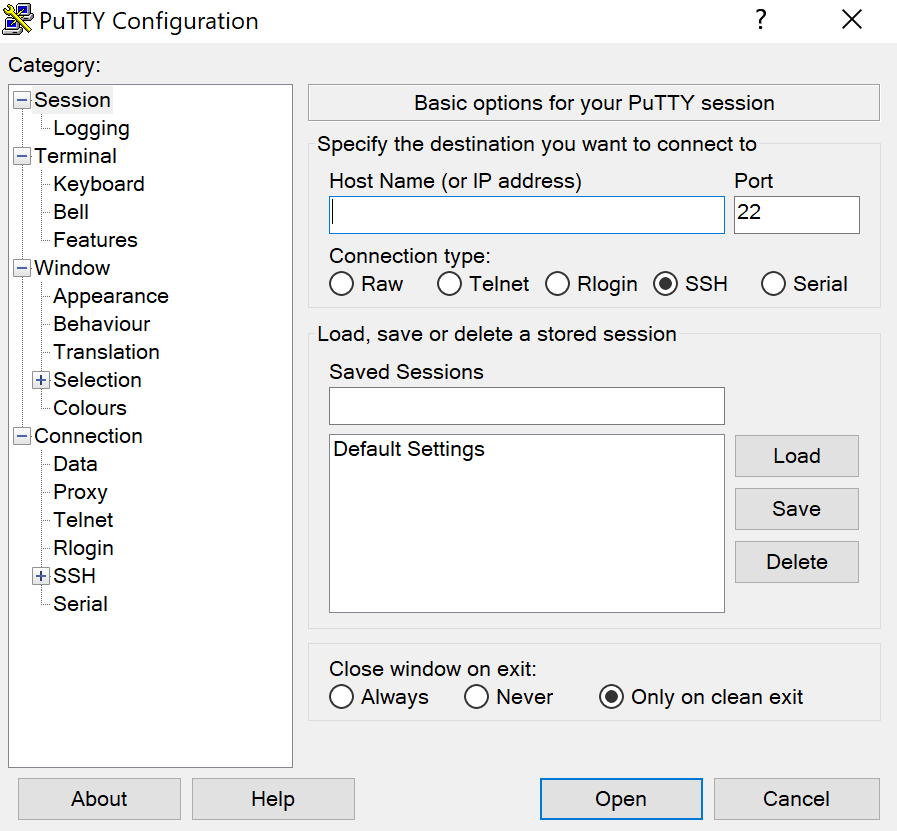
After entering the details, click the Open button. PuTTY will attempt to connect to the server.
If this is your first time connecting, PuTTY may display a security warning about the server’s host key. This is normal. Confirm the prompt to continue.
After the connection is established, a terminal window will open and prompt you to log in.
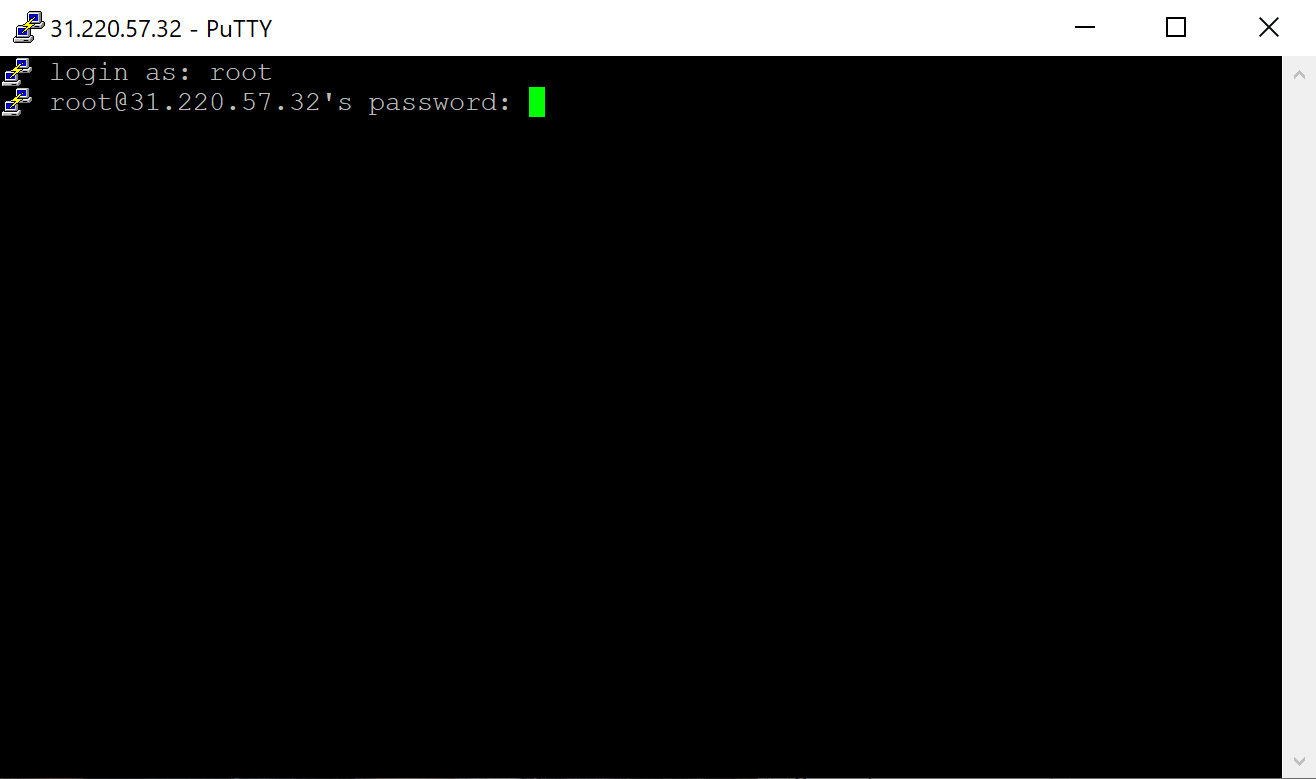
Enter the SSH username when prompted and press Enter. Next, enter the SSH password. For security reasons, the password will not be displayed on the screen while typing.
Once the correct credentials are provided, you will be logged in to the remote server.
At this point, you can begin executing commands to configure the system, check logs, perform diagnostics, or manage files.
Conclusion
TCP port 22 is far more than just a number. It is the foundation of secure remote access through SSH. By combining the reliability of TCP with strong encryption and authentication, SSH over TCP port 22 enables safe device configuration, effective troubleshooting, and detailed diagnostics.
For IT, industrial, and SCADA systems, TCP port 22 supports day-to-day operations and rapid problem resolution while protecting sensitive systems from unauthorized access. Understanding its role and securing it properly is a key part of building reliable and secure networks.
