GOOSE messages are high-speed Ethernet signals used in modern substations to share protection and control information between devices. Although they may look technical, decoding them with Wireshark is actually very easy. With just a few filters and clicks, you can see events, state changes, and dataset values in real time.
In this guide, you’ll learn step-by-step how to capture and decode IEC 61850 GOOSE traffic so you can troubleshoot, commission, or simply understand IEC 61850 systems much more confidently.
Table of Contents
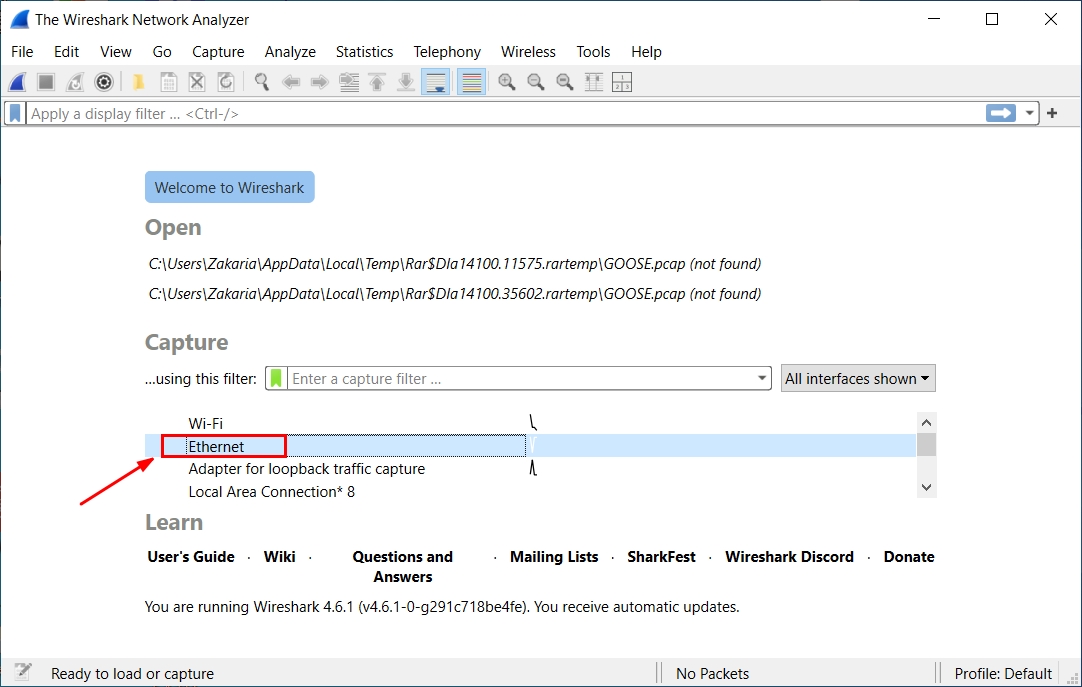
Step 1 : Open Wireshark and Select Your Network Interface
Choose the network card that is connected to your substation/test network.
If you’re unsure which one to pick:
- Look for the interface with traffic activity
- Avoid Wi-Fi unless your GOOSE traffic is bridged to it (usually it’s not)
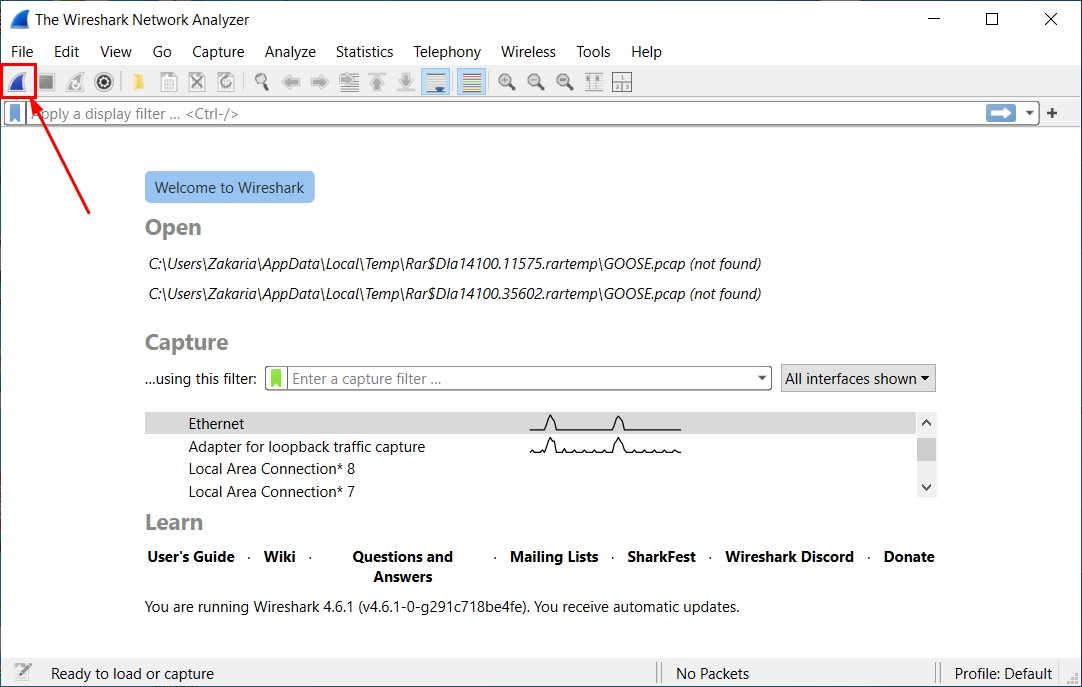
Step 2 : Start the Capture
Click Start Capturing Packets (the blue shark fin icon). You’ll immediately see frames scrolling by.
Step 3 : Set a Capture Filter for Only GOOSE Traffic
In the “Capture Filter” box, type:
goose
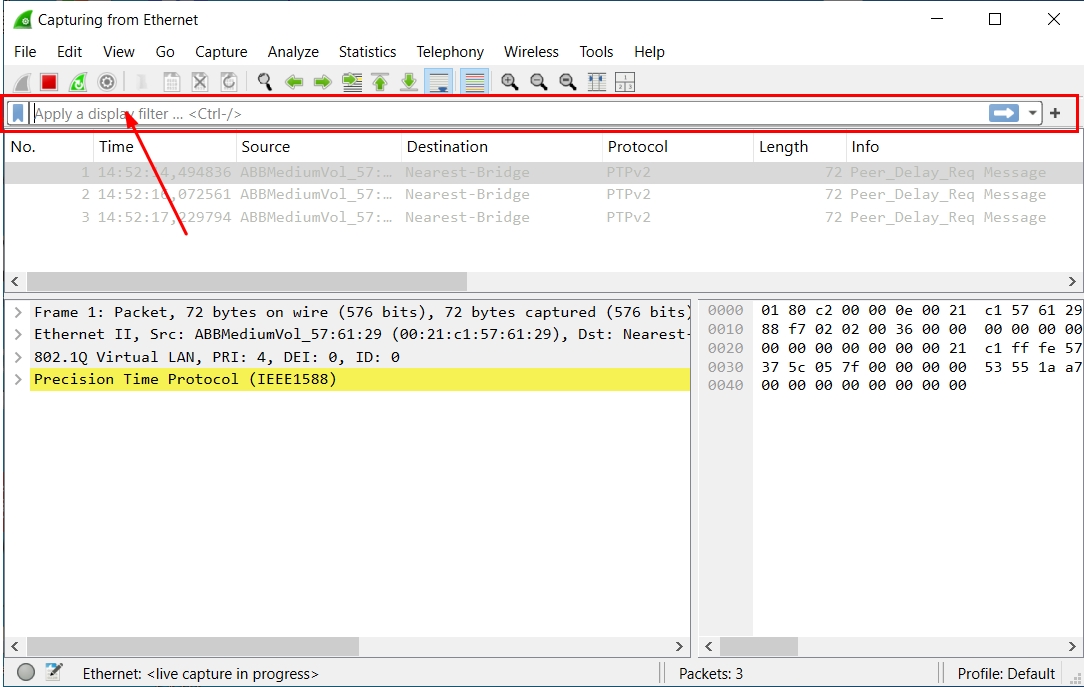
Hit Enter, and the packet list will show only GOOSE frames.
Step 4 : Select a GOOSE Packet to Decode
Click the first packet in the list.
You will see three panes:
- Packet List (top)
- Packet Details (middle)
- Packet Bytes (bottom)
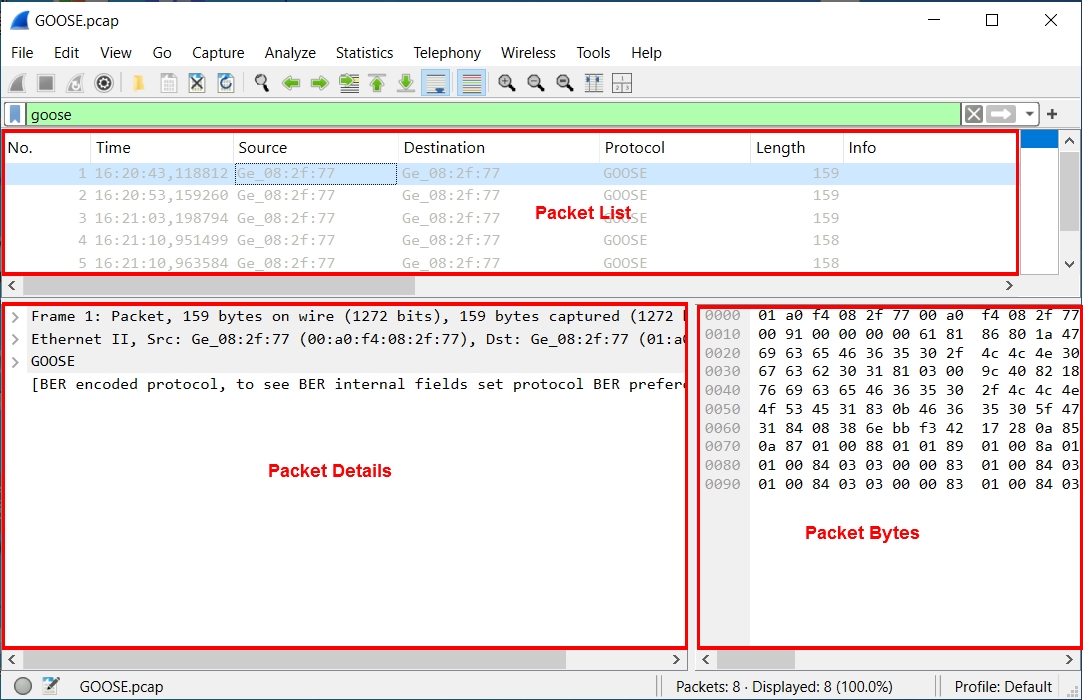
We only need the middle pane for decoding.
Step 5 : Expand the Ethernet II Header
This shows important fields:
- Destination MAC: Multicast (starts with
01:0C:CD…) - Source MAC: Publisher IED
- EtherType:
0x88B8(this confirms it is a GOOSE frame)
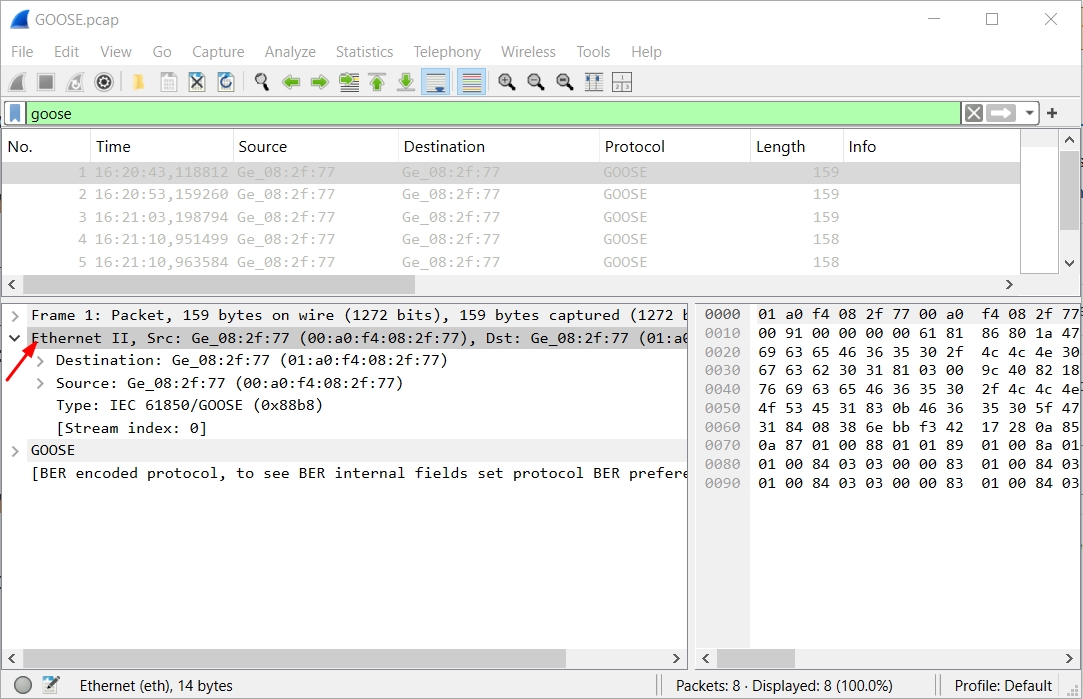
Step 6 : Expand the GOOSE Protocol Section
This is where the real decoding happens.
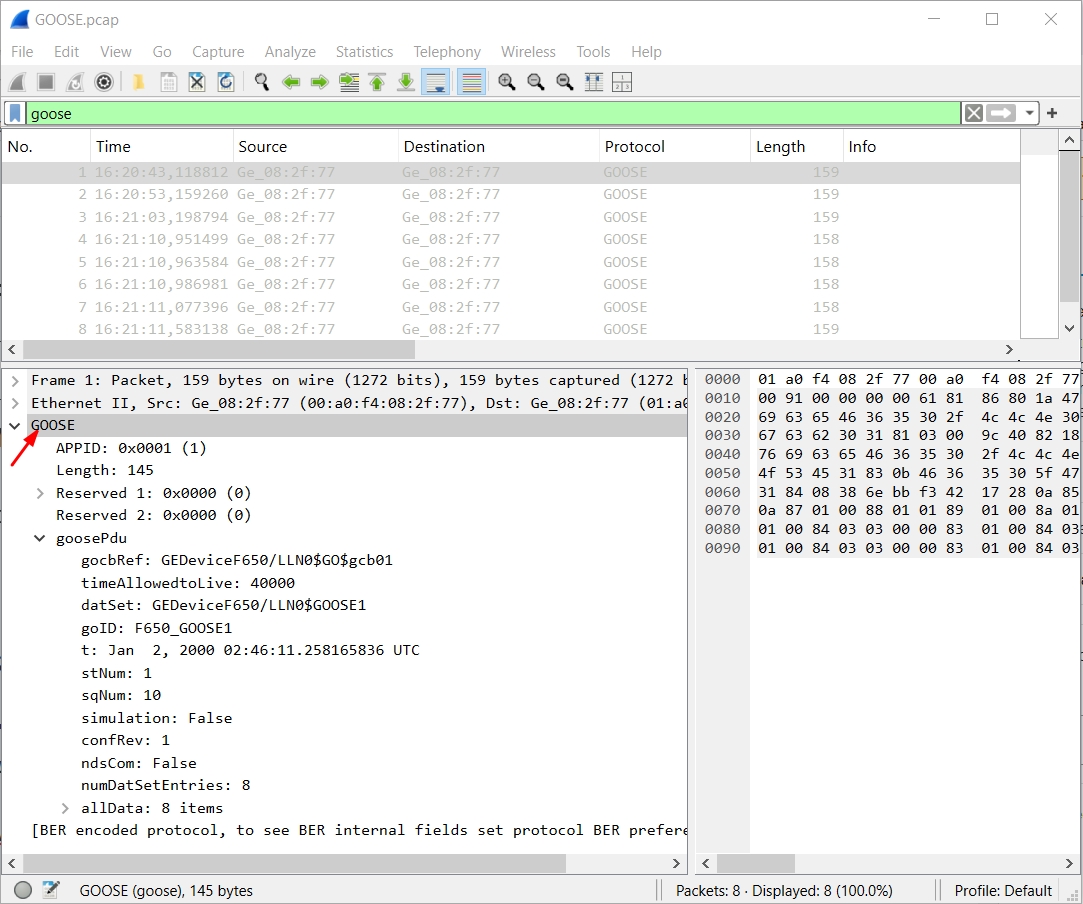
You’ll find key fields:
- gocbRef → GOOSE control block reference
- datSet → Dataset name
- goID → Publisher’s GOOSE ID
- stNum → State Number
- sqNum → Sequence Number
- timeAllowedToLive → How long the message is valid
- Test flag
- ConfRev
- Dataset values (status, analogs, etc.)
Step 7 : Identify When an Event Happens
GOOSE messages repeat constantly.
The trick is to watch the stNum and sqNum fields.
✔ Normal operation
stNumstays the samesqNumincrements with each retransmission
✔ Event occurred (trip, open/close, interlock, change)
- stNum jumps to a new number
- sqNum resets to 0
- Dataset values may change (e.g., breaker opens)
This is the fastest way to detect substation events.
Step 8 : View Dataset Values
Inside the GOOSE decoder, scroll to the bottom.
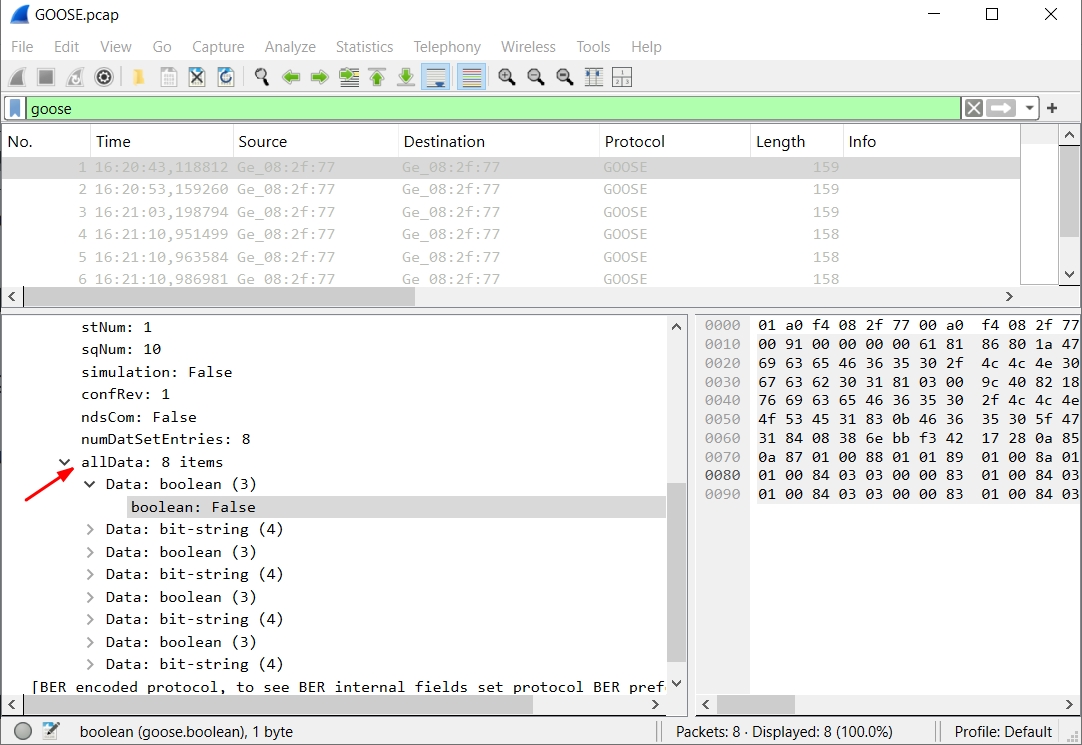
You’ll usually see values such as:
- Boolean statuses
- Analog measurements
- Protection signals
- Interlocking states
These are defined by the device vendor and the IEC-61850 model.
Step 9 : Export Packets for Reporting
You can save the decoded packets:
File → Export Packet Dissections → CSV / TXT / JSON
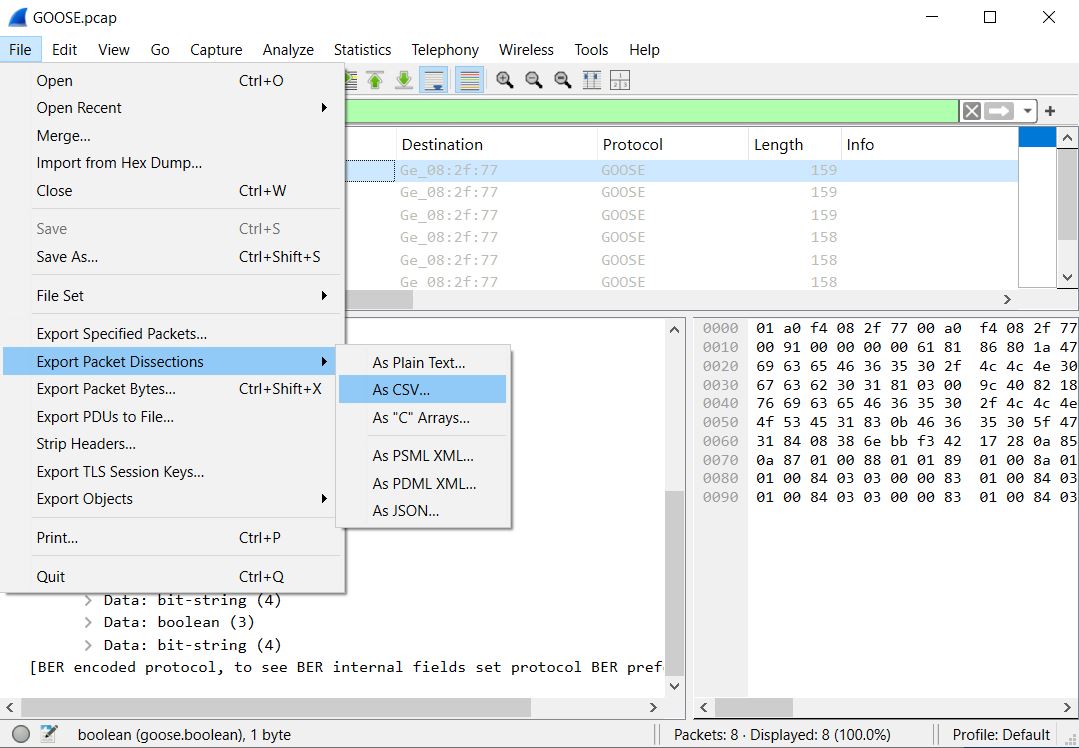
This is perfect for:
- Engineering reports
- Protection studies
- Commissioning documentation
- Forensics after an event
Conclusion
Decoding IEC-61850 GOOSE messages in Wireshark doesn’t have to be complicated. With a few basic filters and an understanding of key fields like stNum, sqNum, and the dataset values, anyone can quickly follow real-time events happening inside a substation network.
Wireshark’s built-in GOOSE dissector makes it easy to spot changes, verify protection behavior, and troubleshoot communication problems without needing advanced IEC-61850 knowledge. Whether you’re commissioning, maintaining, or learning substation automation systems, these steps give you a reliable way to see exactly what your IEDs are sending — clearly, transparently, and in seconds.
💡 Want a deeper understanding of GOOSE and IEC 61850?
Check out our full article: IEC 61850 GOOSE Explained: Complete Guide to Fast Substation Messaging, Protection & Automation.
